Practical Exercise: Diagnosis of Genital Infections Using Microscopy
Objectives: after completing this exercise you should be able to recognise the key microscopic features required to diagnose genital infections.
Instructions: view the embedded digital images (4 cases) and based on both your observations and the associated clinical history, make appropriate comments relevant to a possible diagnosis.
Case 1: 25-year-old female complaining of pelvic pain
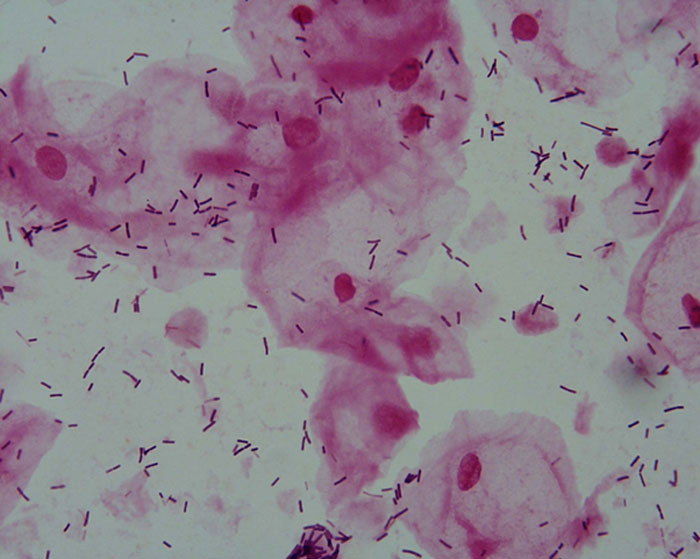
Model answer 1: No abnormalities detected. Lactobacilli and epithelial cells are present.
Case 2: 32-year-old female complaining of vaginal itch and discharge
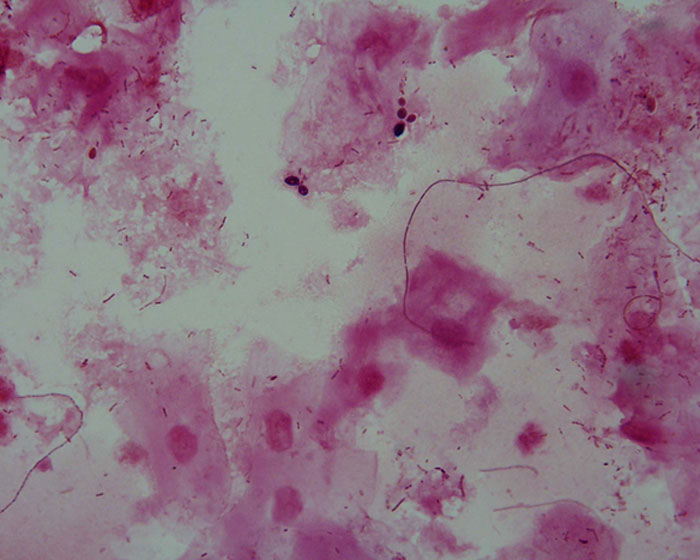
Model answer 2: Yeast cells (probably Candida albicans) are present. This is consistent with Candidiasis (thrush).
Case 3: 24-year-old male presenting with a purulent urethral discharge
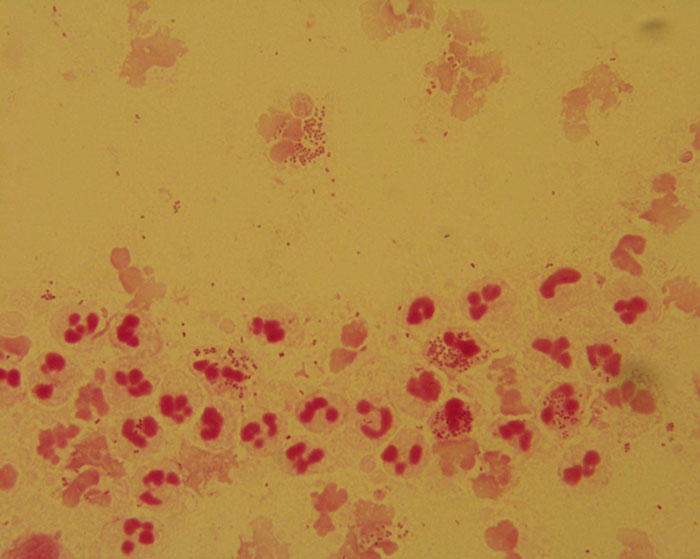
Model answer 3: Numerous white cells are present with many containing intracellular Gram-negative diplococci. This is consistent with a diagnosis of Gonorrhoea.
Case 4: A 25-year-old pregnant female complaining of discharge
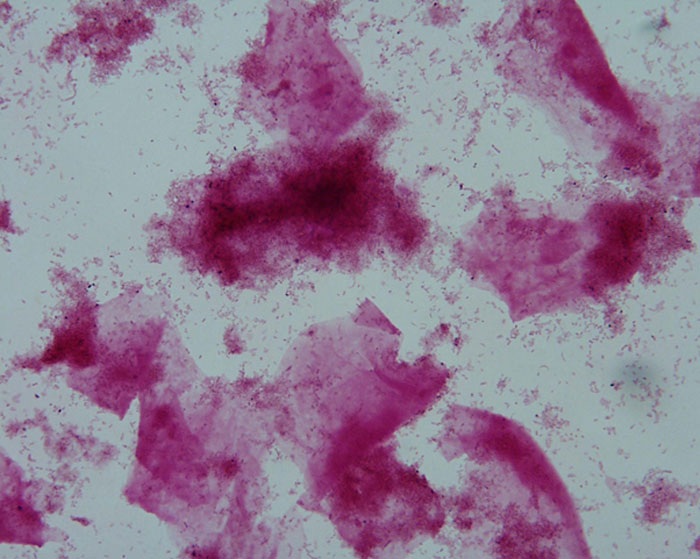
Model answer 4: Lactobacilli are absent, but numerous small Gram-negative bacilli are present, as are "clue cells". This is consistent with a diagnosis of Bacterial Vaginosis.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this page is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International Licence
Note: The open version of this document may have been altered from the original. Only pages on this site that display the CC licence and logo are licensed under a Creative Commons licence.
| Attribution information | |
|---|---|
| Title: | CXA 342 - Medical Microbiology - Practical - Open Version |
| Source: | https://www.utas.edu.au/health/resources/open-resources/resources/courses/laboratory-medicine/cxa-342-medical-microbiology |
| Author: | Dr Stephen Tristram |